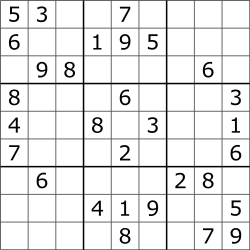
Sudoku
Sudoku (/suːˈdoʊkuː, -ˈdɒk-, sə-/; Japanese: 数独, romanized: sūdoku, lit. 'digit-single'; originally called Number Place)[1] is a logic-based,[2][3] combinatorial[4] number-placement puzzle. In classic Sudoku, the objective is to fill a 9 × 9 grid with digits so that each column, each row, and each of the nine 3 × 3 subgrids that compose the grid (also called "boxes", "blocks", or "regions") contains all of the digits from 1 to 9. The puzzle setter provides a partially completed grid, which for a well-posed puzzle has a single solution.
French newspapers featured similar puzzles in the 19th century, and the modern form of the puzzle first appeared in 1979 puzzle books by Dell Magazines under the name Number Place.[5] However, the puzzle type only began to gain widespread popularity in 1986 when it was published by the Japanese puzzle company Nikoli under the name Sudoku, meaning "single number".[6] In newspapers outside of Japan, it first appeared in The Conway Daily Sun (New Hampshire) in September 2004, and then The Times (London) in November 2004, both of which were thanks to the efforts of the Hong Kong judge Wayne Gould, who devised a computer program to rapidly produce unique puzzles.
History
[edit]
Predecessors
[edit]Number puzzles appeared in newspapers in the late 19th century, when French puzzle setters began experimenting with removing numbers from magic squares. Le Siècle, a Paris daily, published a partially completed 9×9 magic square with 3×3 subsquares on November 19, 1892.[7] It was not a Sudoku because it contained double-digit numbers and required arithmetic rather than logic to solve, but it shared key characteristics: each row, column, and subsquare added up to the same number.
On July 6, 1895, Le Siècle's rival, La France, refined the puzzle so that it was almost a modern Sudoku and named it carré magique diabolique ('diabolical magic square'). It simplified the 9×9 magic square puzzle so that each row, column, and broken diagonals contained only the numbers 1–9, but did not mark the subsquares. Although they were unmarked, each 3×3 subsquare did indeed comprise the numbers 1–9, and the additional constraint on the broken diagonals led to only one solution.[8]
These weekly puzzles were a feature of French newspapers such as L'Écho de Paris for about a decade, but disappeared about the time of World War I.[9]
Modern Sudoku
[edit]The modern Sudoku was most likely designed anonymously by Howard Garns, a 74-year-old retired architect and freelance puzzle constructor from Connersville, Indiana, and first published in 1979 by Dell Magazines as Number Place (the earliest known examples of modern Sudoku).[1] Garns' name was always present on the list of contributors in issues of Dell Pencil Puzzles and Word Games that included Number Place and was always absent from issues that did not.[10] He died in 1989 before getting a chance to see his creation as a worldwide phenomenon.[10] Whether or not Garns was familiar with any of the French newspapers listed above is unclear.
The puzzle was introduced in Japan by Maki Kaji (鍜治 真起, Kaji Maki), president of the Nikoli puzzle company, in the paper Monthly Nikolist in April 1984[10] as Sūji wa dokushin ni kagiru (数字は独身に限る), which can be translated as "the digits must be single", or as "the digits are limited to one occurrence" (In Japanese, dokushin means an "unmarried person"). The name was later abbreviated to Sudoku (数独), taking only the first kanji of compound words to form a shorter version.[10] "Sudoku" is a registered trademark in Japan[11] and the puzzle is generally referred to as Number Place (ナンバープレース, Nanbāpurēsu) or, more informally, a shortening of the two words, Num(ber) Pla(ce) (ナンプレ, Nanpure). In 1986, Nikoli introduced two innovations: the number of givens was restricted to no more than 32, and puzzles became "symmetrical" (meaning the givens were distributed in rotationally symmetric cells). It is now published in mainstream Japanese periodicals, such as the Asahi Shimbun.
Spread outside Japan
[edit]In 1997, Hong Kong judge Wayne Gould saw a partly completed puzzle in a Japanese bookshop. Over six years, he developed a computer program to produce unique puzzles rapidly.[5]
The first newspaper outside of Japan to publish a Sudoku puzzle The Conway Daily Sun (New Hampshire), which published a puzzle by Gould in September 2004.[12][13]
Gould pitched the idea of publishing Sudoku puzzles to newspapers, offering the puzzles for free in exchange for the newspapers' attributing them to him and linking to his website for solutions and other puzzles.
Knowing that British newspapers have a long history of publishing crosswords and other puzzles, he promoted Sudoku to The Times in Britain, which launched it on November 12, 2004 (calling it Su Doku). The first letter to The Times regarding Su Doku was published the following day on November 13 from Ian Payn of Brentford, complaining that the puzzle had caused him to miss his stop on the tube.[14] Sudoku puzzles rapidly spread to other newspapers as a regular feature.[5][15]
The rapid rise of Sudoku in Britain from relative obscurity to a front-page feature in national newspapers attracted commentary in the media and parody (such as when The Guardian's G2 section advertised itself as the first newspaper supplement with a Sudoku grid on every page).[16] Recognizing the different psychological appeals of easy and difficult puzzles, The Times introduced both, side by side, on June 20, 2005. From July 2005, Channel 4 included a daily Sudoku game in their teletext service. On August 2, the BBC's program guide Radio Times featured a weekly Super Sudoku with a 16×16 grid.

The world's first live TV Sudoku show, Sudoku Live, was a puzzle contest first broadcast on July 1, 2005, on the British pay-television channel Sky One. It was presented by Carol Vorderman. Nine teams of nine players (with one celebrity in each team) representing geographical regions competed to solve a puzzle. Each player had a hand-held device for entering numbers corresponding to answers for four cells. Phil Kollin of Winchelsea, England, was the series grand prize winner, taking home over £23,000 over a series of games. The audience at home was in a separate interactive competition, which was won by Hannah Withey of Cheshire.
Later in 2005, the BBC launched SUDO-Q, a game show that combined Sudoku with general knowledge. However, it used only 4×4 and 6×6 puzzles. Four seasons were produced before the show ended in 2007.

An annual World Sudoku Championship series has been organized by the World Puzzle Federation since 2006, except in 2020 and 2021 during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In 2006, a Sudoku website published a Sudoku tribute song by songwriter Peter Levy,[17] but the MP3 file for downloading the song was removed due to heavy traffic. The Japanese Embassy to some country nominated the song to receive some kind of award from someone, and the Herald Sun newspaper in Melbourne, Australia, said Levy was in discussions with Sony in Japan to release the song as a single on a Sony label.[18]
Sudoku software is very popular on PCs, websites, and mobile phones. It comes with many distributions of Linux. The software has also been released on video game consoles, such as the Nintendo DS, PlayStation Portable, the Game Boy Advance, Xbox Live Arcade, the Nook e-book reader, Kindle Fire tablet, several iPod models, and the iPhone. Many Nokia phones also had Sudoku. In fact, just two weeks after Apple Inc. debuted the online App Store within its iTunes Store on July 11, 2008, nearly 30 different Sudoku games were already in it, created by various software developers, specifically for the iPhone and iPod Touch. One of the most popular video games featuring Sudoku is Brain Age: Train Your Brain in Minutes a Day!. Critically and commercially well-received, it generated particular praise for its Sudoku implementation[19][20][21] and sold more than 8 million copies worldwide.[22] Due to its popularity, Nintendo made a second Brain Age game titled Brain Age2, which has over 100 new Sudoku puzzles and other activities.
In June 2008, an Australian drugs-related jury trial costing over A$ 1 million was aborted when it was discovered that four or five of the twelve jurors had been playing Sudoku instead of listening to the evidence.[23]
Variants
[edit]Variations of grid sizes or region shapes
[edit]Although the 9×9 grid with 3×3 regions is by far the most common, many other variations exist. Sample puzzles can be 4×4 grids with 2×2 regions; 5×5 grids with pentomino regions have been published under the name Logi-5; the World Puzzle Championship has featured a 6×6 grid with 2×3 regions and a 7×7 grid with six heptomino regions and a disjoint region. Larger grids are also possible, or different irregular shapes (under various names such as Suguru, Tectonic, Jigsaw Sudoku etc.). The Times offers a 12×12-grid "Dodeka Sudoku" with 12 regions of 4×3 squares. Dell Magazines regularly publishes 16×16 "Number Place Challenger" puzzles (using the numbers 1–16 or the letters A-P). Nikoli offers 25×25 "Sudoku the Giant" behemoths. A 100×100-grid puzzle dubbed Sudoku-zilla was published in 2010.[24]
Mini Sudoku
[edit]Under the name "Mini Sudoku", a 6×6 variant with 3×2 regions appears in the American newspaper USA Today and elsewhere. The object is the same as that of standard Sudoku, but the puzzle only uses the numbers 1 through 6. A similar form, for younger solvers of puzzles, called "The Junior Sudoku", has appeared in some newspapers, such as some editions of The Daily Mail.
Imposing additional constraints
[edit]Another common variant is to add limits on the placement of numbers beyond the usual row, column, and box requirements. Often, the limit takes the form of an extra "dimension"; the most common is to require the numbers in the main diagonals of the grid to also be unique. The aforementioned "Number Place Challenger" puzzles are all of this variant, as are the Sudoku X puzzles in The Daily Mail, which use 6×6 grids.
Killer sudoku
[edit]The killer sudoku variant combines elements of sudoku and kakuro. A killer sudoku puzzle is made up of 'cages', typically depicted by boxes outlined with dashes or colours. The sum of the numbers in a cage is written in the top left corner of the cage, and numbers cannot be repeated in a cage.
Other variants
[edit]Puzzles constructed from more than two grids are also common. Five 9×9 grids that overlap at the corner regions in the shape of a quincunx is known in Japan as Gattai 5 (five merged) Sudoku. In The Times, The Age, and The Sydney Morning Herald, this form of puzzle is known as Samurai Sudoku. The Baltimore Sun and the Toronto Star publish a puzzle of this variant (titled High Five) in their Sunday edition. Often, no givens are placed in the overlapping regions. Sequential grids, as opposed to overlapping, are also published, with values in specific locations in grids needing to be transferred to others.

A tabletop version of Sudoku can be played with a standard 81-card Set deck (see Set game). A three-dimensional Sudoku puzzle was published in The Daily Telegraph in May 2005. The Times also publishes a three-dimensional version under the name Tredoku. Also, a Sudoku version of the Rubik's Cube is named Sudoku Cube.
Many other variants have been developed.[25][26][27] Some are different shapes in the arrangement of overlapping 9×9 grids, such as butterfly, windmill, or flower.[28] Others vary the logic for solving the grid. One of these is "Greater Than Sudoku". In this, a 3×3 grid of the Sudoku is given with 12 symbols of Greater Than (>) or Less Than (<) on the common line of the two adjacent numbers.[10] Another variant on the logic of the solution is "Clueless Sudoku", in which nine 9×9 Sudoku grids are each placed in a 3×3 array. The center cell in each 3×3 grid of all nine puzzles is left blank and forms a tenth Sudoku puzzle without any cell completed; hence, "clueless".[28] Examples and other variants can be found in the Glossary of Sudoku.
Mathematics of Sudoku
[edit]
This section refers to classic Sudoku, disregarding jigsaw, hyper, and other variants. A completed Sudoku grid is a special type of Latin square with the additional property of no repeated values in any of the nine blocks (or boxes of 3×3 cells).[29]
The general problem of solving Sudoku puzzles on n2×n2 grids of n×n blocks is known to be NP-complete.[30] Many Sudoku solving algorithms, such as brute force-backtracking and dancing links can solve most 9×9 puzzles efficiently, but combinatorial explosion occurs as n increases, creating practical limits to the properties of Sudokus that can be constructed, analyzed, and solved as n increases. A Sudoku puzzle can be expressed as a graph coloring problem.[31] The aim is to construct a 9-coloring of a particular graph, given a partial 9-coloring.
The fewest clues possible for a proper Sudoku is 17.[32] Tens of thousands of distinct Sudoku puzzles have only 17 clues.[33]
The number of classic 9×9 Sudoku solution grids is 6,670,903,752,021,072,936,960, or around 6.67×1021.[34] The number of essentially different solutions, when symmetries such as rotation, reflection, permutation, and relabelling are taken into account, is much smaller, 5,472,730,538.[35]
Unlike the number of complete Sudoku grids, the number of minimal 9×9 Sudoku puzzles is not precisely known. (A minimal puzzle is one in which no clue can be deleted without losing the uniqueness of the solution.) However, statistical techniques combined with a puzzle generator show that about (with 0.065% relative error) 3.10 × 1037 minimal puzzles and 2.55 × 1025 nonessentially equivalent minimal puzzles exist.[36]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Grossman, Lev (Mar 11, 2013). "The Answer Men". Time. New York. Archived from the original on 2013-03-01. Retrieved 2013-03-04.(registration required)
- ^ Arnoldy, Ben. "Sudoku Strategies". The Christian Science Monitor.
- ^ Schaschek, Sarah (Mar 22, 2006). "Sudoku champ's surprise victory". The Prague Post. Archived from the original on 2006-08-13. Retrieved 2009-02-18.
- ^ Gradwohl, Ronen; Naor, Moni; Pinkas, Benny; Rothblum, Guy N. (2007). "Cryptographic and Physical Zero-Knowledge Proof Systems for Solutions of Sudoku Puzzles". In Crescenzi, Pierluigi; Prencipe, Giuseppe; Pucci, Geppino (eds.). Fun with Algorithms, 4th International Conference, FUN 2007, Castiglioncello, Italy, June 3-5, 2007, Proceedings. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 4475. Springer. pp. 166–182. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-72914-3_16. ISBN 978-3-540-72913-6.
- ^ a b c Smith, David (May 15, 2005). "So you thought Sudoku came from the Land of the Rising Sun ..." The Observer. Retrieved 2008-06-13.
The puzzle gripping the nation actually began at a small New York magazine
- ^ Hayes, Brian (2006). "Unwed Numbers". American Scientist. 94 (1): 12–15. doi:10.1511/2006.57.3475.
- ^ Boyer, Christian (May 2006). "Supplément de l'article "Les ancêtres français du sudoku"" (PDF). Pour la Science (in French): 1–6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-12-10. Retrieved 2009-08-03.
- ^ Boyer, Christian (2007). "Sudoku's French ancestors" (in French). (personal webpage). Archived from the original on 2007-10-10. Retrieved 2009-08-03.
- ^ Malvern, Jack (Jun 3, 2006). "Les fiendish French beat us to Su Doku". The Times. Retrieved 2024-10-02.
- ^ a b c d e Pegg, Ed Jr. (Sep 15, 2005). "Ed Pegg Jr.'s Math Games: Sudoku Variations". MAA Online. The Mathematical Association of America. Retrieved 2006-10-03.
- ^ "Reg. No. 5056856". Japanese Trademark 5056856. Japan Platform for Trademark Information. Retrieved 2018-10-03.
- ^ "Correction attached to "Inside Japan's Puzzle Palace"". The New York Times. Mar 21, 2007.
- ^ "The rise and rise of Sudoku". The Independent. Apr 10, 2006.
- ^ Payn, Ian (Nov 13, 2004). "Deep in thought". The Times.
- ^ Devlin, Keith (Jan 28–29, 2012). "The Numbers Game (book review of Taking Sudoku Seriously by Jason Rosenhouse et al.)". The Wall Street Journal. p. C5.
- ^ "G2, home of the discerning Sudoku addict". The Guardian. London. May 13, 2005. Retrieved 2006-09-16.
- ^ "Sudoku the song, by Peter Levy". Sudoku.org.uk. Aug 17, 2006. Retrieved 2008-10-05.
- ^ "Hit Song Has the Numbers". The Herald Sun. Aug 17, 2006. Retrieved 2008-10-05.[dead link]
- ^ "Brain Age: Train Your Brain in Minutes a Day!". Gamerankings.com.
- ^ "Brain Age: ... Review". Gamespot.com.
- ^ Harris, Craig (Apr 18, 2006). "Brain Age: Train Your Brain in Minutes a Day". IGN. Retrieved 2023-02-08.
- ^ Thorsen, Tor (Oct 26, 2006). "Nintendo posts $456.6 million profit". GameSpot. Retrieved 2013-03-29.
- ^ Knox, Malcolm (Jun 11, 2008). "The game's up: jurors playing Sudoku abort trial". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 2008-06-11.
- ^ Eisenhauer, William (2010). Sudoku-zilla. CreateSpace. p. 220. ISBN 978-1-4515-1049-2.
- ^ Snyder, Thomas; Huang, Wei-Hwa (2009). Mutant Sudoku. Puzzlewright Press. ISBN 978-1-402765025.
- ^ Conceptis, Puzzles (2013). Amazing Sudoku Variants. Puzzlewright. ISBN 978-1454906520. OCLC 700343731.
- ^ Murali, A V (2014). A Collection of Fascinating Games and Puzzles. CreateSpace Independent Publishing. ISBN 978-1500216429. OCLC 1152132274.
- ^ a b "Zahlenraetsel". janko.at.
- ^ Keedwell, A. D. (Nov 2006). "Two remarks about Sudoku squares". The Mathematical Gazette. 90 (519): 425–430. doi:10.1017/s0025557200180234. JSTOR 40378190.
- ^ Yato, Takayuki; Seta, Takahiro (2003). "Complexity and completeness of finding another solution and its application to puzzles" (PDF). IEICE TRANSACTIONS on Fundamentals of Electronics, Communications and Computer Sciences. E86-A (5): 1052–1060. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-03-03.
- ^ Lewis, R. (2015). A Guide to Graph Colouring: Algorithms and Applications. Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-25730-3. ISBN 978-3-319-25728-0. OCLC 990730995. S2CID 26468973.
- ^ McGuire, G.; Tugemann, B.; Civario, G. (2014). "There is no 16-Clue Sudoku: Solving the Sudoku Minimum Number of Clues Problem". Experimental Mathematics. 23 (2): 190–217. arXiv:1201.0749. doi:10.1080/10586458.2013.870056.
- ^ Royle, Gordon. "Minimum Sudoku". Archived from the original on 2006-11-26. Retrieved 2012-02-28.
- ^ Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A107739 (Number of (completed) sudokus (or Sudokus) of size n^2 X n^2)". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation.
- ^ Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A109741 (Number of inequivalent (completed) n^2 X n^2 sudokus (or Sudokus))". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation.
- ^ Berthier, Denis (Dec 4, 2009). "Unbiased Statistics of a CSP – A Controlled-Bias Generator". In Elleithy, Khaled (ed.). Innovations in Computing Sciences and Software Engineering. Springer. pp. 165–70. Bibcode:2010iics.book.....S. doi:10.1007/978-90-481-9112-3. ISBN 978-90-481-9111-6. Retrieved 2009-12-04.
Further reading
[edit]- Delahaye, Jean-Paul (Jun 2006). "The Science Behind Sudoku" (PDF). Scientific American. 294 (6): 80–87. Bibcode:2006SciAm.294f..80D. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0606-80. JSTOR 26061494. PMID 16711364.
- Provan, J. Scott (Oct 2009). "Sudoku: Strategy Versus Structure". American Mathematical Monthly. 116 (8): 702–707. doi:10.4169/193009709X460822. S2CID 38433481. Also as UNC/STOR/08/04.